Latest Articles
Ready, Healthy & Able
The number of active-duty women in the military has grown exponentially in recent years and is expected to continue to increase.
Did you know?
- 17% of all active duty service members are women
- The number of active duty servicewomen is expected to increase by 18,000 women per year over the next decade
- Women are 28% more likely to leave the military than their male counterparts
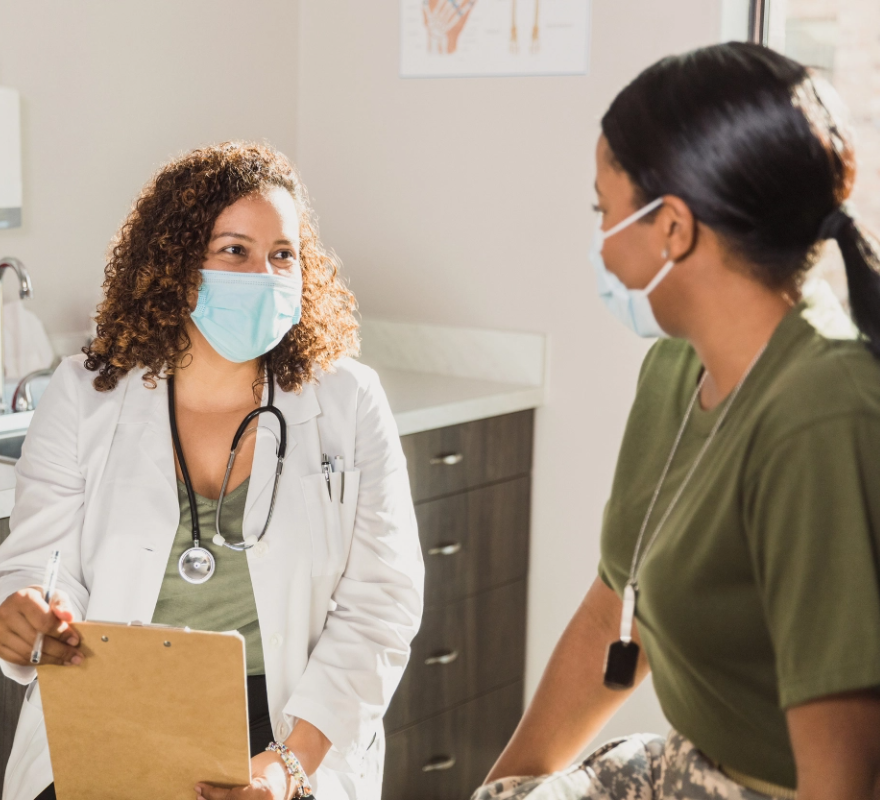
But despite this increase in servicewomen, the military’s healthcare services are struggling to evolve and accommodate their unique needs. HealthyWomen’s Ready, Healthy & Able program aims to help address that problem and keep servicewomen healthy and fit for duty.
Health Topics
Learn how to address the unique health challenges facing women in the military
Real Women, Real Stories
Read personal stories about the health journeys of servicewomen like you

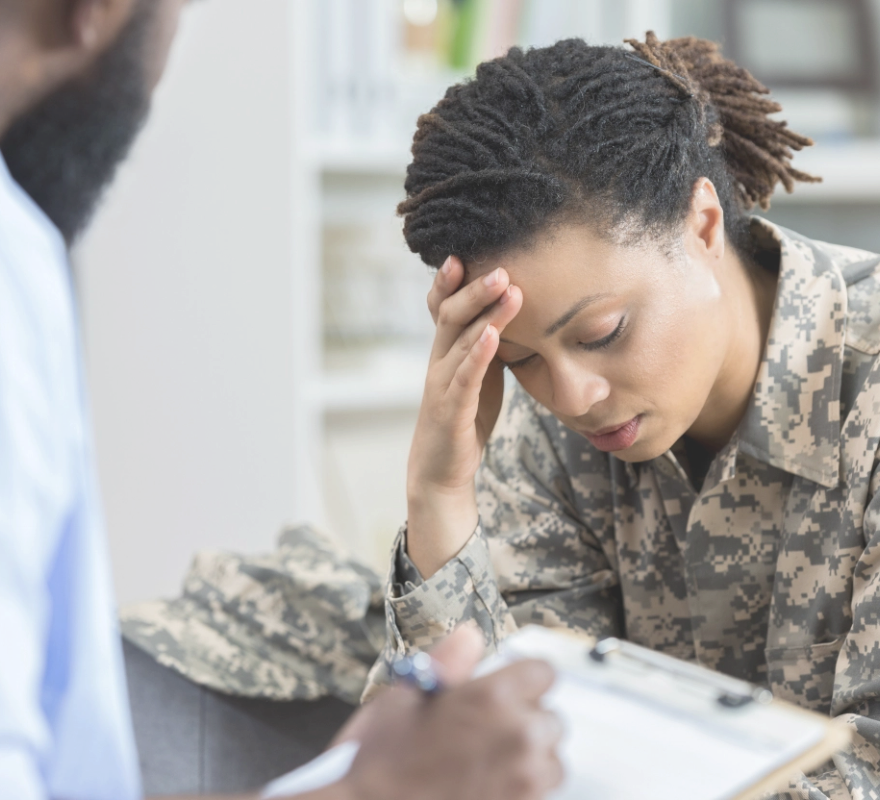
Just As My Husband Went to War Overseas, My War Began at Home
Now I work to make sure other cancer warriors are battle-ready

I Loved My Army and Air Force Career, but the Toll It Took on My Health Was Brutal
After my experience with healthcare in the military, I’m now committed to getting veterans fair treatment
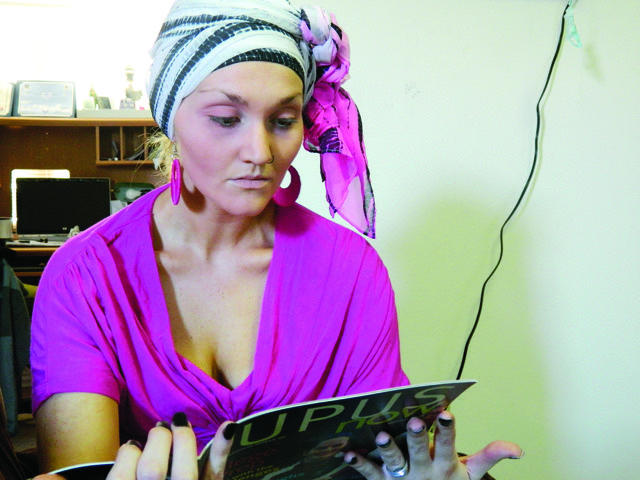

It Wasn’t Stress. It Was Lupus.
Every time I was told I was “just working too hard,” the misdiagnosis allowed my body to continue damaging itself
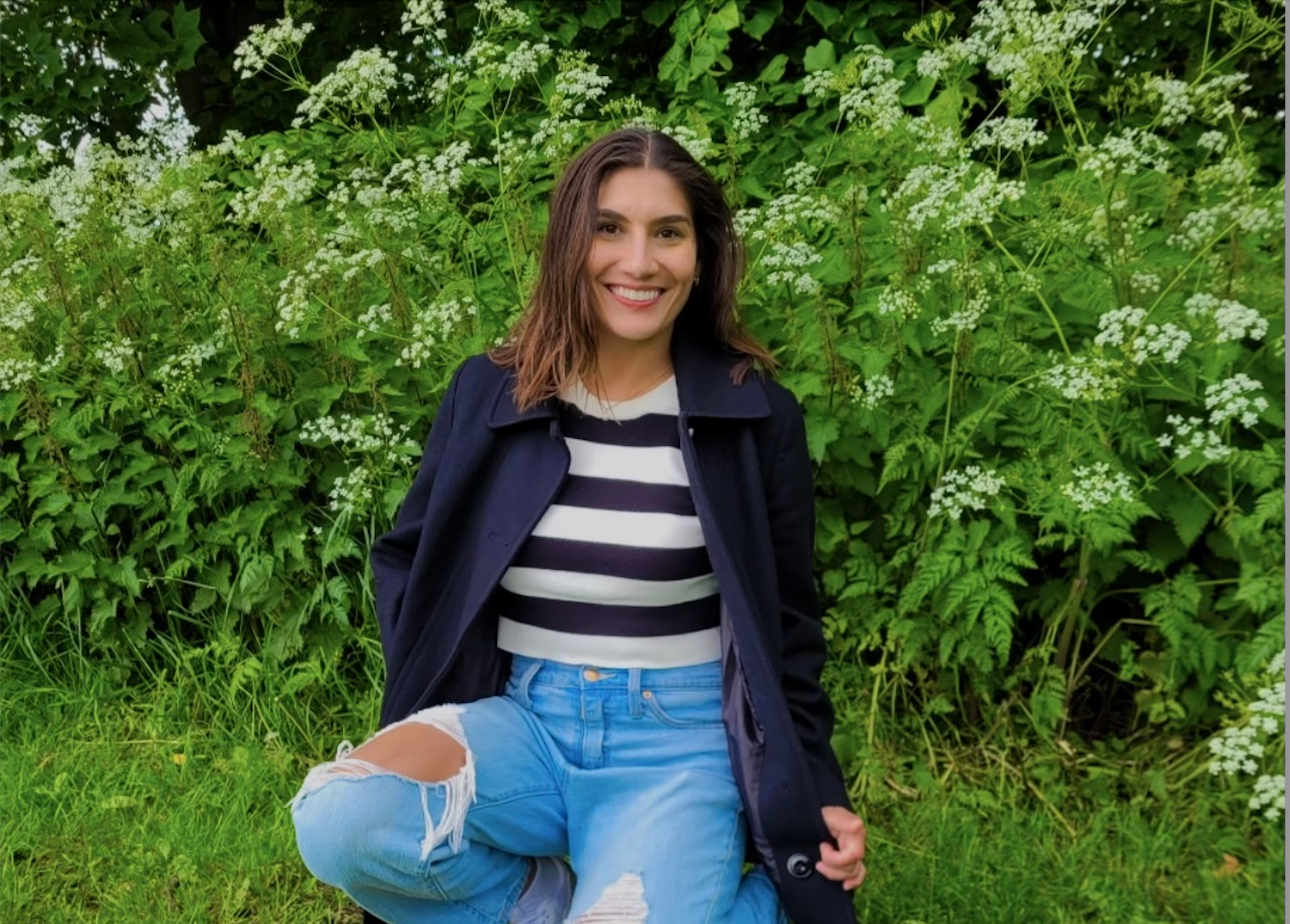

Military Doctors Told Me I Was Fine — But I Had Lupus
I got so sick that I ended up intubated in the ICU
En Español

Justo cuando mi esposo fue a una guerra en otro país, una guerra empezó en mi hogar
Ahora trabajo para asegurarme que otras personas que luchan contra el cáncer estén listas para esa batalla
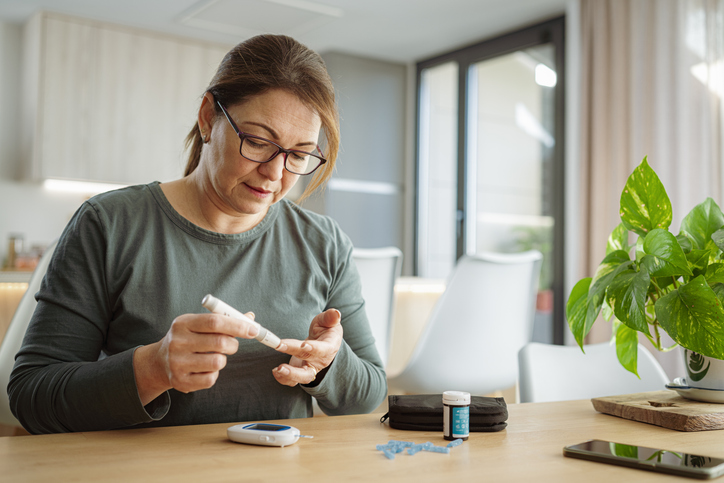

El control de la diabetes después del servicio militar
La transición cuando termina el servicio militar puede incrementar tu riesgo de diabetes

Amé mi carrera en el ejército y en la fuerza aérea, pero la carga que impuso en mi salud fue brutal
Después de mi experiencia con la atención médica en las fuerzas armadas, tengo el compromiso de hacer que los veteranos reciban un trato justo

El cáncer de mama implica desafíos únicos para las veteranas
El cáncer de mama es un diagnóstico difícil y para mujeres que trabajaron en las fuerzas armadas es demasiado frecuente